Is America Becoming a Land of Haves and Have-Nots?
Income inequality in the United States has been a persistent and growing issue. Here are 12 eye-opening statistics that highlight the income inequality crisis in America as of September 2022:
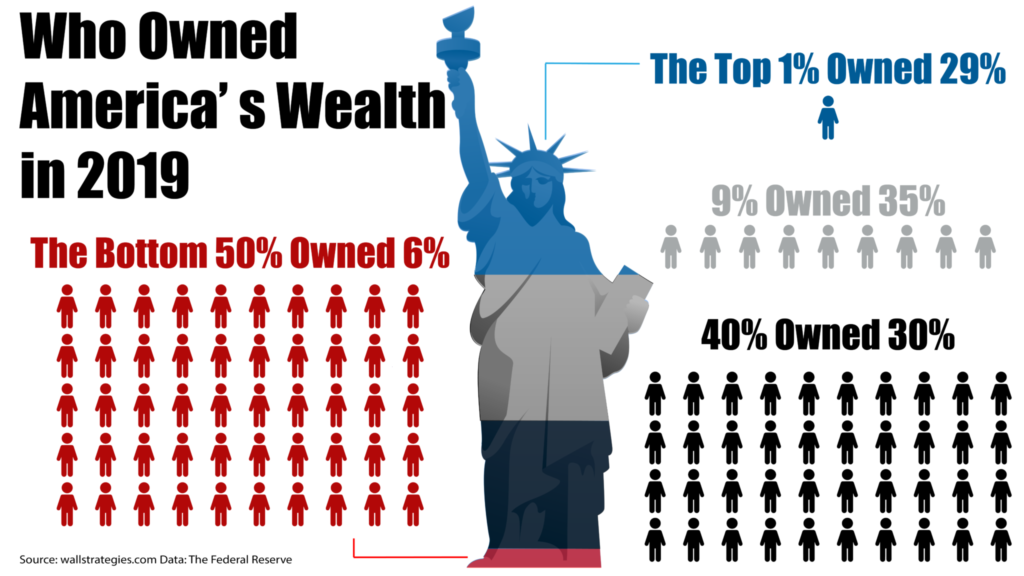
- Wealth Concentration at the Top: In 2020, the wealthiest 1% of Americans held over 31% of the country’s total wealth, while the bottom 50% collectively owned just 2% of the wealth, according to the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances.
- Income Share of the Top 10%: The top 10% of income earners in the U.S. received approximately 48% of the nation’s total income in 2019, according to the World Inequality Database.
- CEO-to-Worker Pay Gap: In 2020, CEOs of S&P 500 companies earned approximately 299 times more than the average worker’s salary, according to the Economic Policy Institute.
- Income Growth for the Wealthiest: Between 1979 and 2017, the income of the top 1% of income earners in the U.S. grew by 157%, while the income of the bottom 90% grew by just 22%, according to the Economic Policy Institute.
- Income Mobility: Research by the National Bureau of Economic Research indicates that income mobility in the U.S. is relatively low, with children’s incomes strongly correlated with their parents’ incomes.
- Poverty Rates: In 2020, approximately 9.1% of Americans were living below the poverty line, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. Poverty rates are on the rise among all US populations.
- Student Loan Debt: As of 2021, outstanding student loan debt in the U.S. surpassed $1.5 trillion, with many graduates facing substantial debt burdens that can hinder their financial well-being.
- Access to Healthcare: Lack of access to affordable healthcare is a contributing factor to income inequality. In 2020, about 9% of the U.S. population remained uninsured, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
Income inequality is a pressing issue that has been plaguing the United States for decades. It refers to the unequal distribution of wealth and income among individuals and households within a society. In recent years, this issue has gained significant attention due to the staggering disparities that have emerged. This article delves into ten eye-opening statistics that shed light on America’s income inequality crisis, providing a comprehensive overview of the magnitude of the problem. By examining the wealth gap, concentration of wealth, disparities based on race and gender, rising poverty rates, the role of education, social mobility, and policy implications, we aim to highlight the urgent need for action to address this deep-rooted issue in American society.
America’s Income Inequality Crisis
Income inequality refers to the unequal distribution of wealth and income among individuals or households in a society. It measures the disparity in earnings and assets, highlighting the gap between the rich and the poor, and is an key factor in the rise of Marxism on college campuses.
The Significance of Income Inequality
Income inequality is not just an abstract concept; it has real consequences for individuals and society as a whole. High levels of income inequality can lead to social and economic instability, hinder upward mobility, and increase social tensions. Understanding and addressing income inequality is crucial for creating a fair and equitable society.
The Growing Wealth Gap: Exploring the Numbers
In the United States, income distribution is heavily skewed towards the top. A small percentage of the population holds a significant portion of the total income, while the majority receives a much smaller share. This unequal distribution has been a growing trend over the past few decades, exacerbating income inequality.
Historical Trends: How the Wealth Gap Has Evolved
Over the years, the wealth gap in America has widened significantly. In the 1970s, the top 1% of earners accounted for around 8% of the national income. Today, that share has more than doubled, with the top 1% now earning approximately 20% of the income. This trend highlights the increasing concentration of wealth among a select few.
Concentration of Wealth: Who Holds the Majority?
The Role of the Top 1%: Examining the Elite
The top 1% of earners in the United States, often referred to as the “economic elite,” hold a disproportionate amount of wealth and income. These individuals, typically CEOs, entrepreneurs, and high-level executives, have seen their earnings skyrocket while the majority of workers’ wages have stagnated.
Income Disparity Across Different Socioeconomic Groups
Income inequality is not solely about the top 1%. It affects individuals across various socioeconomic groups. Middle-class households have experienced sluggish income growth, while those at the bottom of the income scale struggle to make ends meet. Understanding how income disparities impact different groups is crucial for addressing the income inequality crisis.
Rising Poverty Rates: The Impact on American Society
Picture this: your neighbor, the single mom working two jobs just to make ends meet. Or your childhood friend who couldn’t afford college and now struggles to find stable employment. Poverty in America knows no boundaries and affects people from all walks of life. According to eye-opening statistics, the face of poverty is diverse, spanning across different ages, races, and genders. It’s high time we understand the demographics of poverty to truly grasp the magnitude of the issue.
Consequences of Poverty: Effects on Health, Education, and Crime
Poverty is not just a matter of empty pockets; it has far-reaching consequences that ripple through society. When individuals are trapped in poverty, their health suffers, their educational opportunities are limited, and the risk of engaging in criminal activities increases. These intertwining effects create a vicious cycle that perpetuates inequality. It’s not just about dollars and cents; it’s about the toll poverty takes on the well-being and future prospects of our fellow Americans.
Social Mobility and Income Inequality: Is the American Dream Still Attainable?
Measuring Social Mobility: The Reality for Americans
The American Dream, once synonymous with upward mobility and endless possibilities, seems to be slipping away for many Americans. Studies measuring social mobility reveal a harsh truth: the chances of moving up the economic ladder are dwindling, with fewer opportunities to improve one’s circumstances. The dream of a better life is becoming more elusive, leaving many to wonder if it is still attainable.
Barriers to Social Mobility: Factors That Reinforce Inequality
Various factors act as barriers to social mobility, cementing the grip of income inequality. Limited access to quality education, lack of affordable housing, and a dearth of job opportunities are just a few examples of the obstacles faced by those seeking to climb the economic ladder. Unless these barriers are dismantled, income inequality will continue to hinder social mobility, perpetuating a society where the rich get richer, and the poor struggle to escape their circumstances.
Tackling Income Inequality in America
Addressing income inequality requires a multi-faceted strategy that tackles its root causes head-on. From implementing progressive taxation policies to increasing the minimum wage and investing in quality education, a comprehensive approach is needed to bridge the income gap. It’s time for policymakers to step up and enact meaningful change that uplifts all Americans, fostering a more equitable society for future generations.
The Role of Government and Public Support
While individual efforts and community initiatives play crucial roles in addressing income inequality, the government must also play its part. Public support programs, such as affordable healthcare, affordable housing, and food assistance, can provide a safety net for those struggling to make ends meet. By recognizing the importance of public support and implementing effective policies, we can build a society where every individual has a fair chance to thrive and succeed.In conclusion, the eye-opening statistics presented in this article paint a stark picture of the income inequality crisis in America. The growing wealth gap, disparities based on race and gender, rising poverty rates, and the impact on social mobility reveal the urgent need for comprehensive policy changes. By acknowledging and addressing these issues, we can strive towards a more equitable society that provides equal opportunities for all. It is only through collective effort, awareness, and policy reforms that we can work towards bridging the income gap and creating a more just and inclusive America for future generations.

